The Ethereum network secures billions of dollars of value 24/7, 365. How?
People all over the world lock away (or “stake”) ether (ETH) in smart contracts to run the software that processes Ethereum transactions and secures the Ethereum network. In return, they get rewarded with more ETH.
Restaking is a technology built for stakers to extend this security to other services, applications, or networks. In return, they earn additional restaking rewards. However, they also put their staked ETH at more risk.
Restaking explained in 18 minutes
What is restaking?
Restaking is when stakers use their already-staked ETH to secure other decentralized services. In return, restakers can get additional rewards from those other services on top of their regular ETH staking rewards.
The decentralized services secured by restaking are known as "Actively Validated Services" (AVSs). In the same way that many ETH stakers run Ethereum validation software, many restakers run specialized AVS software.
Good to know
While "Actively Validated Services" (AVSs) is the most common, different restaking platforms may use other names for the decentralized services they help secure, like "Autonomously Validated Services," "Distributed Secure Services," or "Networks."
Staking vs restaking
| Staking | Restaking |
|---|---|
| Earn ETH rewards | Earn ETH Rewards + AVS rewards |
| Secures the Ethereum network | Secures the Ethereum network + AVSs |
| No minimum ETH | No minimum ETH |
| Low risk level | Low-to-high risk level |
| Withdraw time depends on queue | Withdraw time depends on queue + unbonding period |
Why do we need restaking?
Picture two worlds; one with restaking and one without.
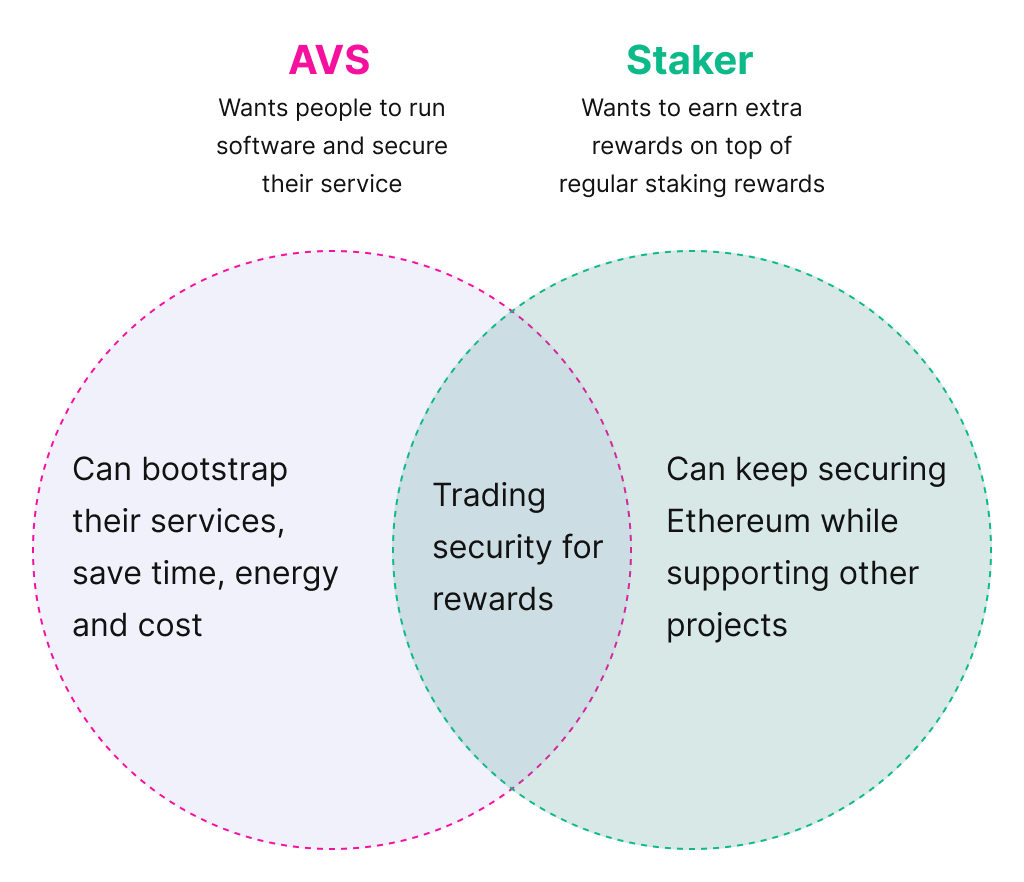
In this world with restaking, both the AVS and staker benefit from being able to find each other and trade security for extra rewards.
Added benefit of restaking
AVSs can pour all their resources into building and marketing their services, instead of getting distracted with decentralization and security.
How does restaking work?
There are several entities involved in restaking — each one of them plays an important part.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Restaking platforms | A restaking platform is a service that connects AVSs, ETH stakers, and operators. They build decentralized applications for stakers to restake their ETH, and marketplaces where stakers, AVSs, and operators can find each other. |
| Native restakers | People who stake their ETH by running their own Ethereum validators can connect their staked ETH to a restaking platform, including EigenLayer and others, to earn restaking rewards on top of ETH validator rewards. |
| Liquid restakers | People who stake their ETH via a third-party liquid staking provider, like Lido or Rocket Pool, get Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) that represent their staked ETH. They can restake these LSTs to earn restaking rewards while keeping their original ETH staked. |
| Operators | Operators run the AVSs' restaking software, performing the validation tasks each AVS requires. Operators are usually professional service providers that guarantee things like uptime and performance. Like non-operator restakers, operators use staked ETH to secure AVSs, but operators also receive extra rewards in exchange for their work. |
| AVSs | These are the decentralized services — like price oracles, token bridges, and data systems — that receive security from restakers and offer token rewards in return. |
Good to know
Native and liquid restakers often delegate their staked ETH to an operator, instead of running the software to secure AVSs themselves.
This way they don't need to worry about complicated technical requirements from AVSs, though they receive a lower reward rate than operators.
What are some examples of restaking?
While a novel idea, a few projects have emerged to explore the possibilities of restaking.
 EigenLayer (Restaking Platform)
EigenLayer (Restaking Platform)EigenLayer introduced the idea of restaking in 2023 and has grown to thousands of people restaking millions of ETH. Referred to as “Ethereum middleware”, it connects stakers, operators and AVSs.
 Symbiotic (Restaking platform)
Symbiotic (Restaking platform)Symbiotic is a permissionless restaking protocol that helps secure different blockchain networks by letting users “restake” their assets.
Misnomer alert
Some people confuse "restaking" with lending and borrowing LSTs in DeFi. Both put staked ETH to work, but restaking means securing AVSs, not just earning yield on LSTs.
How much can I make from restaking?
While AVSs offer different rates, Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs) like eETH give you an idea of how much you can make. In the same way you get LSTs like stETH for staking your ETH, you can get LRTs like eETH for restaking stETH. These tokens earn ETH staking and restaking rewards.
It’s important to acknowledge the risks with restaking. The potential rewards can be attractive, but they’re not risk free.
What are the risks of restaking?
| Risks | Description |
|---|---|
| Penalties (or “slashing”) | Like ETH staking, if restakers/operators go offline, censor messages or try to corrupt the network, their stake can be slashed (burned) partially or entirely. |
| Centralization | If few operators dominate most of the restaking they could have a great influence on restakers, AVSs and even restaking platforms. |
| Chain reactions | If a restaker gets slashed while securing multiple AVSs, this could lower the security for the other AVSs, making them vulnerable. |
| Immediate access to funds | There is a wait time (or “unbonding period”) for withdrawing restaked ETH so you may not always have access immediately. |
The Ethereum co-founder is typing…
Vitalik, the co-founder of Ethereum, warned about the potential risks of restaking in a 2021 blog post called Don't Overload Consensus.
How to get started with restaking?
| 🫡 Beginners | 🤓 Advanced Users |
|---|---|
| 1. Stake ETH on platforms like Lido or Rocket Pool to get LSTs. | 1. Stake your ETH as a validator on Ethereum. |
| 2. Use those LSTs to start restaking on a restaking service. | 2. Compare restaking services like EigenLayer, Symbiotic and others. |
| 3. Follow the instructions to connect your validator to the restaking smart contract. |
Ethereum Staking : How does it work?
Learn MoreAdvanced
Further reading
- ethereum.org - ETH staking guide
- Ledger Academy - What Is Ethereum Restaking?opens in a new tab
- Consensys - EigenLayer: Decentralized Ethereum Restaking Protocol Explainedopens in a new tab
- Vitalik Buterin - Don't overload Ethereum's consensusopens in a new tab
- Cointelegraph - What is EigenLayer? Ethereum’s restaking protocol explainedopens in a new tab
- a16z crypto research - EigenLayer: Permissionless Feature Addition to Ethereum with Sreeram Kannanopens in a new tab
- Junion - EigenLayer Explained: What is Restaking?opens in a new tab
- The Block - Restaking Data Dashopens in a new tab
Page last update: February 25, 2026