Solidity and Truffle continuous integration setup
Continuous integration (CI) with Truffle is great for developing once you have a basic set of tests implemented. It allows you to run very long tests, ensure all tests pass before merging a pull request(opens in a new tab) and to keep track of various statistics using additional tools.
We will use the Truffle Metacoin Box(opens in a new tab) to setup our continuous integration. You can either choose Travis CI or Circle CI.
Setting up Travis CI
Adding Travis CI(opens in a new tab) is straight-forward. You will only need to add a .travis.yml config file to the root folder of the project:
1language: node_js2node_js:3 - 1045cache: npm67before_script:8 - echo fs.inotify.max_user_watches=524288 | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf && sudo sysctl -p910script:11 - npm testZobraziť všetko
We are keeping it simple for now and are only running the test script which executes the Truffle unit tests. But we have one problem, there won't be a blockchain available on the Travis CI machine. A simple fix for this is to npm install ganache-cli and simply run it before the test. You can do this by adding a bash script with the line npx ganache-cli > /dev/null and before the npx truffle test call. The full example bash script(opens in a new tab).
Setting up Circle CI
CircleCi(opens in a new tab) requires a longer config file. The additional npm ci(opens in a new tab) command is automatically done in Travis. It installs dependencies faster and more securely than npm install does. We again use the same script from the Travis version to run ganache-cli before the tests.
1version: 223aliases:4 - &defaults5 docker:6 - image: circleci/node:1078 - &cache_key_node_modules9 key: v1-node_modules-{{ checksum "package-lock.json" }}1011jobs:12 dependencies:13 <<: *defaults14 steps:15 - checkout16 - restore_cache:17 <<: *cache_key_node_modules18 - run:19 name: Install npm dependencies20 command: |21 if [ ! -d node_modules ]; then22 npm ci23 fi24 - persist_to_workspace:25 root: .26 paths:27 - node_modules28 - build29 - save_cache:30 paths:31 - node_modules32 <<: *cache_key_node_modules3334 test:35 <<: *defaults36 steps:37 - checkout38 - attach_workspace:39 at: .40 - run:41 name: Unit tests42 command: npm test4344workflows:45 version: 246 everything:47 jobs:48 - dependencies49 - test:50 requires:51 - dependenciesZobraziť všetko
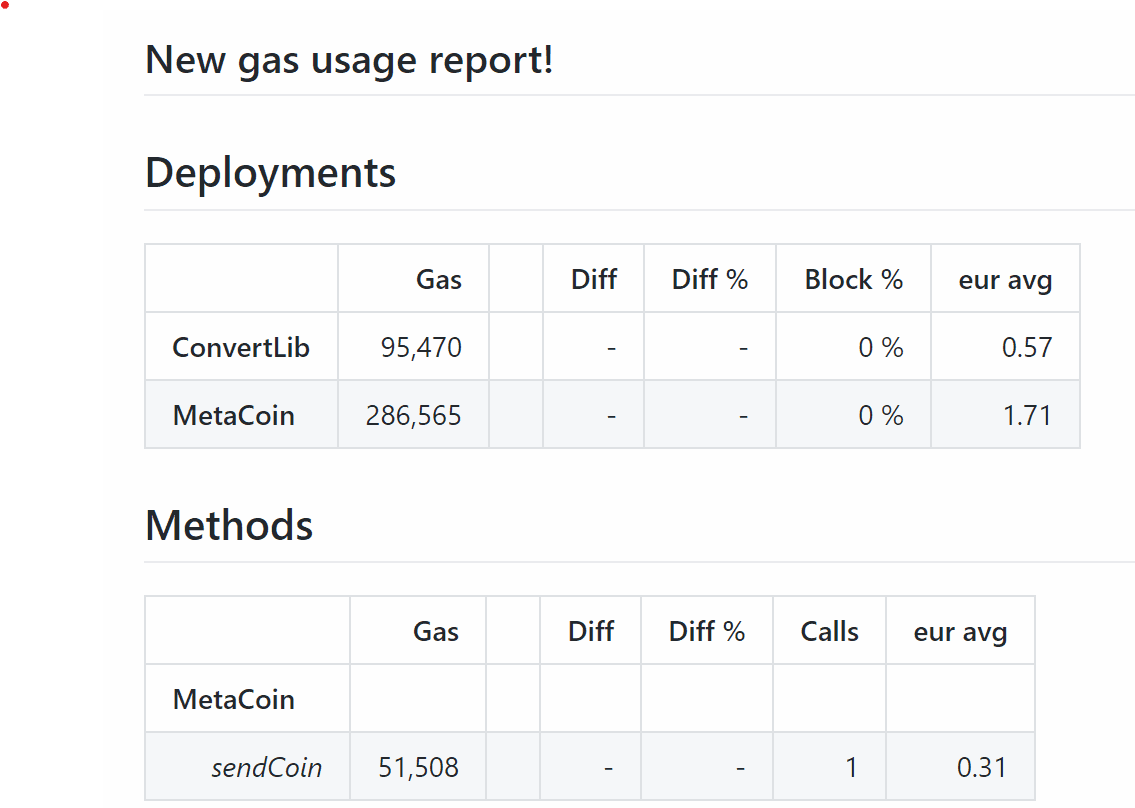
Adding the eth-gas-reporter plugin
The eth-gas-reporter plugin is quite useful for keeping track of the gas costs of your smart contract functions. Having it in your CI will further be useful for showing diffs when adding pull requests.
Step 1: Install the eth-gas-reporter plugin and codechecks
npm install --save-dev eth-gas-reporternpm install --save-dev @codechecks/client
Step 2: Add the plugin to the mocha settings inside your truffle-config.js
See options(opens in a new tab)
1module.exports = {2 networks: { ... },3 mocha: {4 reporter: 'eth-gas-reporter',5 reporterOptions: {6 excludeContracts: ['Migrations']7 }8 }9};Zobraziť všetkoKopírovať
Step 3: Add a codechecks.yml to your project's root directory
1checks:2 - name: eth-gas-reporter/codechecks
Step 4: Run codechecks after the test command
- npm test- npx codechecks
Step 5: Create a Codechecks account
- Create an account with Codechecks(opens in a new tab).
- Add the GitHub repo to it.
- Copy the secret and add the
CC_SECRET=COPIED SECRETto your CI (see here for Travis(opens in a new tab), here for CircleCi(opens in a new tab)). - Now go ahead and create a pull request.
That's it. You will now find a nice report about changes in gas costs of your pull request.
Adding the solidity-coverage plugin
With the solidity-coverage plugin you can check how much of your code paths are covered by your tests. Adding this to your CI makes is very convenient to use once it is set up.
Step 1: Create a metacoin project and install coverage tools
npm install --save-dev truffle coveralls solidity-coverage
Step 2: Add solidity-coverage to the plugins array in truffle-config.js
1module.exports = {2 networks: {...},3 plugins: ["solidity-coverage"]4}Kopírovať
Step 3: Add the coverage commands to the .travis.yml or Circle CI config.yml
- npx truffle run coverage- cat coverage/lcov.info | npx coveralls
Solidity coverage starts its own ganache-cli, so we don't have to worry about this. Do not replace the regular test command though, coverage's ganache-cli works differently and is therefore no replacement for running regular unit tests.
Step 4: Add repository to coveralls
- Create an account with Coveralls(opens in a new tab).
- Add the GitHub repo to it.
- Now go ahead and create a pull request.
Further ideas
- MythX(opens in a new tab): With MythX you can automatically analyze your smart contract security. So it makes a lot of sense to add this to your CI(opens in a new tab).
- Linting(opens in a new tab): Good code can be enforced to some degree with linting tools. Eslint(opens in a new tab) works great for JavaScript, is easy to setup(opens in a new tab), while Solhint(opens in a new tab) can be used for Solidity.
- Long tests: Sometimes you may want to add extreme tests, e.g., testing a contracts with hundreds of users. This takes a lot of time. Instead of running those in every test run, add them to the CI.
There you have it. Continuous integration is a very useful strategy for your developments. You can check out a full example at Truffle-CI-Example(opens in a new tab). Just make sure to remove Circle-CI or Travis, one is enough!
Naposledy editované: @nhsz(opens in a new tab), 15. augusta 2023