离线数据完整性的默克尔证明
简介
理想的情况下,我们想要将所有东西存储在以太坊存储器中。这些数据存储于数以千计的计算机中 且有极高的可用性(数据不会被审查)和完整性(不能在未经授权的情况下修改数据), 但存储一个 32 字节的词一般需要花费 20,000 燃料。 在撰写此教程时,该费用 等于 6.60 美元。 每字节 21 美分对许多应用程序来说都过于昂贵。
为了解决这个问题,以太坊生态系统开发了许多以去中心化方式存储数据的 代替方法。 通常情况下, 需要在可用性与价格之间进行取舍。 然而,完整性通常可以得到保证。
本篇文章中,你将学习如何在以下情况下确保数据的完整性:不将数据存储在区块链上,而是使用 Merkle 证明。
工作原理
理论上,我们只需要存储链上数据的哈希值,然后将所有数据发送到需要这些数据的交易中。 但是,这会非常昂贵。 1 字节的数据通过交易发送的成本约 16 个燃料,目前约 0.5 美分,或每千字节约 5 美元。 每兆字节 5,000 美元,这对于许多应用程序来说仍然太昂贵,而且还没有加上对数据进行哈希计算的费用。
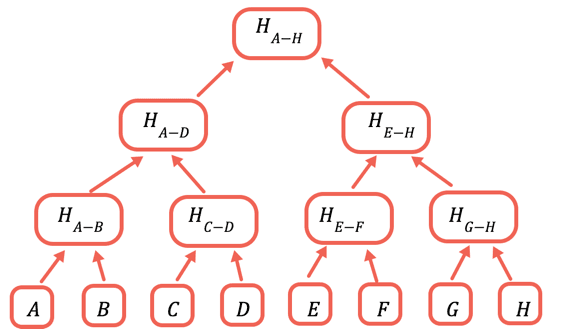
解决办法是反复对不同的数据子集进行哈希计算。对于不需要发送的数据,只要发送哈希值即可。 默克尔树是一种树型数据结构,每个节点值都是其下方节点的哈希值:
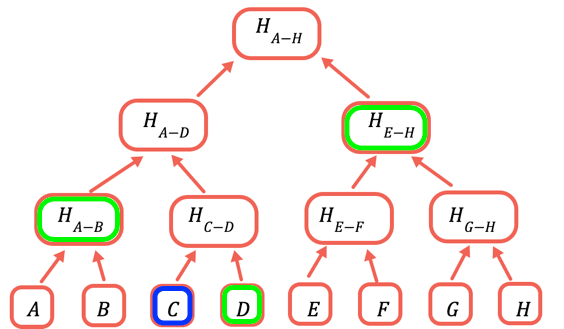
根哈希是唯一需要存储在链上的部分。 为了证明一个特定值,你需要提供所有与之合并才能获取根的哈希值。 例如,要证明 C,你需要提供 D、H(A-B) 和 H(E-H)。
实现
链下代码
在这篇文章中,我们使用 JavaScript 进行链下计算。 大多数去中心化应用程序的 JavaScript 中都有链下组件。
创建默克尔根
首先,我们需要向区块链提供默克尔根。
1const ethers = require("ethers")1// The raw data whose integrity we have to verify. The first two bytes a2// are a user identifier, and the last two bytes the amount of tokens the3// user owns at present.4const dataArray = [5 0x0bad0010, 0x60a70020, 0xbeef0030, 0xdead0040, 0xca110050, 0x0e660060,6 0xface0070, 0xbad00080, 0x060d0091,7]例如,将每条数据编码为单个 256 位整数,并以非 JSON 的格式存储。 然而,这意味着在提取合约中的数据时,可以大大减少处理工作,从而显著降低了燃料成本。 你可以在链上读取 JSON 格式的数据,但请尽量避免这么做。
1// The array of hash values, as BigInts2const hashArray = dataArray在此例中,我们的数据开始就是 256 位,因此不需要处理。 如果我们使用更复杂的数据结构,如字符串,我们需要确保先取数据的哈希值并获取哈希数组。 请注意,还有一个原因是我们不关心用户是否知道其他用户的信息。 否则,我们将不得不进行散列计算,使用户 1 不知道用户 0 的值,用户 2 不知道用户 3 的值,等等。
1// Convert between the string the hash function expects and the2// BigInt we use everywhere else.3const hash = (x) =>4 BigInt(ethers.utils.keccak256("0x" + x.toString(16).padStart(64, 0)))以太币哈希函数的预期结果是一个带十六进制数字的 JavaScript 字符串,如 0x60A7,并用另一个相同结构的字符串响应。 然而,对于代码的其他部分,使用 BigInt 类型更为容易,所以我们将转换为一个十六进制字符串,然后再转回 BigInt。
1// Symmetrical hash of a pair so we won't care if the order is reversed.2const pairHash = (a, b) => hash(hash(a) ^ hash(b))此函数是对称的(a xor b 的哈希值)。 这意味着在检查默克尔证明时,我们不必烦恼是将证明中的值放在计算值之前还是之后。 默克尔证明在链上进行检查,所以链上的步骤越少越好。
警告: 密码学没有表面看起来那么容易。 本文的初始版本提供了哈希函数 hash(a^b)。 那是一个糟糕的想法,因为这意味着如果知道 a 和 b 的合法值,则可以使用 b' = a^b^a' 证明任何所需的 a' 值。 使用此函数,就必须计算 b',令 hash(a') ^ hash(b') 等于一个已知值(通往根的下一个分支),这要困难得多。
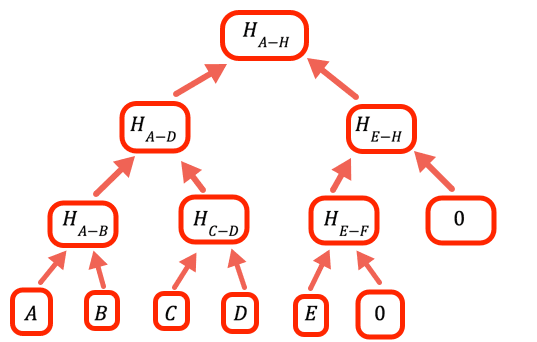
1// The value to denote that a certain branch is empty, doesn't2// have a value3const empty = 0n如果值的数量不是 2 的整数次方,我们需要处理空分支。 该程序的处理方式是将 0 作为占位符。
1// Calculate one level up the tree of a hash array by taking the hash of2// each pair in sequence3const oneLevelUp = (inputArray) => {4 var result = []5 var inp = [...inputArray] // To avoid over writing the input // Add an empty value if necessary (we need all the leaves to be // paired)67 if (inp.length % 2 === 1) inp.push(empty)89 for (var i = 0; i < inp.length; i += 2)10 result.push(pairHash(inp[i], inp[i + 1]))1112 return result13} // oneLevelUp显示全部此函数通过对默克尔树中当前层级的值对进行哈希处理来上升一个层级。 请注意,这不是最高效的实现。我们本来可以避免重复输入,并且只需在循环中适当地加上 hashEmpty,但此代码为了提高可读性进行过优化。
1const getMerkleRoot = (inputArray) => {2 var result34 result = [...inputArray] // Climb up the tree until there is only one value, that is the // root. // // If a layer has an odd number of entries the // code in oneLevelUp adds an empty value, so if we have, for example, // 10 leaves we'll have 5 branches in the second layer, 3 // branches in the third, 2 in the fourth and the root is the fifth56 while (result.length > 1) result = oneLevelUp(result)78 return result[0]9}显示全部要到达根,一直上升到只剩下一个值的层级。
创建一个默克尔证明
默克尔证明是与要证明的值一起哈希处理以便返回默克尔根的值。 要证明的值往往来自其他数据,因此这里更愿意单独提供,而不是作为代码的一部分。
1// A merkle proof consists of the value of the list of entries to2// hash with. Because we use a symmetrical hash function, we don't3// need the item's location to verify the proof, only to create it4const getMerkleProof = (inputArray, n) => {5 var result = [], currentLayer = [...inputArray], currentN = n67 // Until we reach the top8 while (currentLayer.length > 1) {9 // No odd length layers10 if (currentLayer.length % 2)11 currentLayer.push(empty)1213 result.push(currentN % 214 // If currentN is odd, add with the value before it to the proof15 ? currentLayer[currentN-1]16 // If it is even, add the value after it17 : currentLayer[currentN+1])18显示全部我们对 (v[0],v[1])、(v[2],v[3]) 等进行哈希处理。 因此,对于偶数值,我们需要下一个值,而奇数值则需要上一个值。
1 // Move to the next layer up2 currentN = Math.floor(currentN/2)3 currentLayer = oneLevelUp(currentLayer)4 } // while currentLayer.length > 156 return result7} // getMerkleProof链上代码
最后,我们有核查证明的代码。 链上代码用 Solidity 语言编写。 优化在这里更为重要,因为燃料费相对昂贵。
1//SPDX-License-Identifier: Public Domain2pragma solidity ^0.8.0;34import "hardhat/console.sol";编写此代码时,我使用的是安全帽开发环境,它使我们在开发过程中可以获得 Solidity 的控制台输出。
12contract MerkleProof {3 uint merkleRoot;45 function getRoot() public view returns (uint) {6 return merkleRoot;7 }89 // Extremely insecure, in production code access to10 // this function MUST BE strictly limited, probably to an11 // owner12 function setRoot(uint _merkleRoot) external {13 merkleRoot = _merkleRoot;14 } // setRoot显示全部为默克尔根设置和获取函数。 在生产系统中,让每个人都更新默克尔根是一个_非常糟糕的主意_。 这里这样做是为了简化示例代码。 不要在数据完整性非常重要的系统上执行。
1 function hash(uint _a) internal pure returns(uint) {2 return uint(keccak256(abi.encode(_a)));3 }45 function pairHash(uint _a, uint _b) internal pure returns(uint) {6 return hash(hash(_a) ^ hash(_b));7 }此函数生成一个配对哈希值。 它只是将 hash 和 pairHash 函数的 JavaScript 代码转变为 Solidity。
**注意:**这是又一次对可读性的优化。 根据函数定义,也许可以将数据存储为 bytes32 类型值并避免转换。
1 // Verify a Merkle proof2 function verifyProof(uint _value, uint[] calldata _proof)3 public view returns (bool) {4 uint temp = _value;5 uint i;67 for(i=0; i<_proof.length; i++) {8 temp = pairHash(temp, _proof[i]);9 }1011 return temp == merkleRoot;12 }1314} // MarkleProof显示全部用数学符号表示,默克尔证明的验证看起来像这样:H(proof_n, H(proof_n-1, H(proof_n-2, ... H(proof_1, H(proof_0, value))...))). 此代码实现了默克尔证明。
默克尔证明和卷叠很难混淆
默克尔证明对卷叠的作用不大。 原因在于,卷叠将所有交易数据写入一层网络,但在二层网络进行处理。 发送交易的默克尔证明的成本平均达到每个层级 638 个燃料(目前,如果字节不为零,调用数据中一个字节花费 16 个燃料,如果为零,则花费 4 个燃料)。 如果我们的数据包含 1024 个字,默克尔证明需要 10 个层级,或者总共 6380 个燃料。
举一个乐观卷叠的示例,写入一层网络的燃料成本约为 100 gwei,写入二层网络的成本为 0.001 gwei(这里按正常价格计,成本可能因为网络拥塞而增加)。 所以对于一层网络上 1 个燃料的成本,我们可能需要在二层网络上花费 10 万个燃料的处理费用。 假定我们不用重写存储,这意味着我们可以用一个一层网络燃料的价格将大约五个字写入二层网络的存储中。 对于单个默克尔证明,我们可以将全部 1024 个字写入存储(假定它们可以在链上计算出来,而不是在交易中提供),并且还剩下大部分燃料。
总结
在现实中,你可能永远不会独立实现默克尔树。 有很多广为人知并经过审核的程序库可供使用,一般来说,最好不要自己独立实现加密基元。 但我希望你们现在能够更好地理解默克尔证明,并能够决定何时值得使用。
请注意,虽然默克尔证明能维持_完整性_,但并不维持_可用性_。 如果数据存储方决定禁止访问,而且你不能构建默克尔树来访问你的资产,那么知道没有人可以拿走你的资产也只能作为一种小小的慰藉而已。 所以默克尔树最好和某种去中心化存储一起使用,例如星际文件系统。